Логистическое распределение
| Логистическое распределение | |
|---|---|
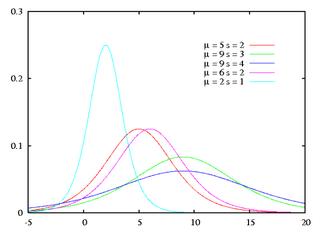 Плотность вероятности Плотность вероятности | |
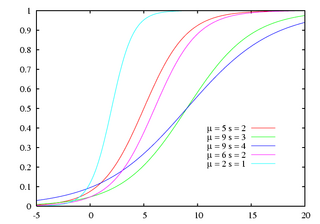 Функция распределения Функция распределения | |
| Обозначение | [math]\displaystyle{ L(\mu,s) }[/math] |
| Параметры |
[math]\displaystyle{ \mu }[/math] [math]\displaystyle{ s\gt 0 }[/math] |
| Носитель | [math]\displaystyle{ x \in (-\infty; +\infty) }[/math] |
| Плотность вероятности | [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{e^{-(x-\mu)/s}} {s\left(1+e^{-(x-\mu)/s}\right)^2} }[/math] |
| Функция распределения | [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{1}{1+e^{-(x-\mu)/s}} }[/math] |
| Математическое ожидание | [math]\displaystyle{ \mu }[/math] |
| Медиана | [math]\displaystyle{ \mu }[/math] |
| Мода | [math]\displaystyle{ \mu }[/math] |
| Дисперсия | [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{\pi^2}{3} s^2 }[/math] |
| Коэффициент асимметрии | [math]\displaystyle{ 0 }[/math] |
| Коэффициент эксцесса | [math]\displaystyle{ 6/5 }[/math] |
| Дифференциальная энтропия | [math]\displaystyle{ \ln(s)+2 }[/math] |
| Производящая функция моментов |
[math]\displaystyle{ e^{\mu\,t}\,\mathrm{B}(1-s\,t,\;1+s\,t) }[/math] для [math]\displaystyle{ |s\,t|\lt 1 }[/math], Бета-функция |
| Характеристическая функция |
[math]\displaystyle{ e^{i \mu t}\,\mathrm{B}(1-ist,\;1+ist) }[/math] для [math]\displaystyle{ |ist|\lt 1 }[/math] |
Логисти́ческое распределе́ние в теории вероятностей и математической статистике — один из видов абсолютно непрерывных распределений. Формой напоминает нормальное распределение, но имеет более «тяжёлые» концы и больший коэффициент эксцесса.
Определение
Функция плотности
Функция плотности вероятности логистического распределения задаётся формулой:
- [math]\displaystyle{ f(x; \mu,s) = \frac{e^{-(x-\mu)/s}} {s\left(1+e^{-(x-\mu)/s}\right)^2} }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ =\frac{1}{4\,s} \;\operatorname{sech}^2\!\left(\frac{x-\mu}{2\,s}\right). }[/math]
Альтернативная параметризация задается подстановкой [math]\displaystyle{ \sigma^2 = \pi^2\,s^2/3 }[/math]. Тогда функция плотности имеет вид:
- [math]\displaystyle{ g(x;\mu,\sigma) = f(x;\mu,\sigma\sqrt{3}/\pi) = \frac{\pi}{\sigma\,4\sqrt{3}} \,\operatorname{sech}^2\!\left(\frac{\pi}{2 \sqrt{3}} \,\frac{x-\mu}{\sigma}\right). }[/math]
Функция распределения
Кумулятивной функцией распределения является логистическая функция:
- [math]\displaystyle{ F(x; \mu,s) = \frac{1}{1+e^{-(x-\mu)/s}} }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ = \frac12 + \frac12 \;\operatorname{tanh}\!\left(\frac{x-\mu}{2\,s}\right). }[/math]
Квантили
Обратная функция к кумулятивной функции распределения ([math]\displaystyle{ F^{-1} }[/math]), обобщение logit-функции:
- [math]\displaystyle{ F^{-1}(p; \mu,s) = \mu + s\,\ln\left(\frac{p}{1-p}\right). }[/math]
Моменты распределения
Математическое ожидание
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbb{E}[X]=\int_{-\infty}^{\infty} {\frac{xe^{-(x-\mu)/s}} {s\left(1+e^{-(x-\mu)/s}\right)^2}} \! dx = \int_{-\infty}^{\infty} \frac{x}{4\,s} \;\operatorname{sech}^2\!\left(\frac{x-\mu}{2\,s}\right)dx }[/math]
- Подставляем: [math]\displaystyle{ u=\frac{(x-\mu)}{2s}, du=\frac{1}{2s} dx }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbb{E}[X]=\int_{-\infty}^{\infty} \frac{2\,s\,u+\mu}{2} \;\operatorname{sech}^2\!\left(u\right)du }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbb{E}[X]=s\int_{-\infty}^{\infty} u \;\operatorname{sech}^2\!\left(u\right)du + \frac{\mu}{2} \int_{-\infty}^{\infty} \;\operatorname{sech}^2\!\left(u\right)du }[/math]
- Справедливо равенство: [math]\displaystyle{ \int_{-\infty}^{\infty} u \;\operatorname{sech}^2\!\left(u\right)du = 0 }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbb{E}[X]=\frac{\mu}{2} \int_{-\infty}^{\infty} \;\operatorname{sech}^2\!\left(u\right)du = \frac{\mu}{2}\,2 = \mu }[/math]
Моменты высших порядков
Центральный момент n-го порядка может быть вычислен как:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} \mathbb{E}[(X-\mu)^n] &= \int_{-\infty}^\infty (x-\mu)^n dF(x) = \int_0^1 \big(F^{-1}(p)-\mu\big)^n dp \\ &= s^n \int_0^1 \Big[ \ln\!\Big(\frac{p}{1-p}\Big) \Big]^n \, dp. \end{align} }[/math]
Интеграл может быть выражен через числа Бернулли:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbb{E}[(X-\mu)^n] = s^n\pi^n(2^n-2)\cdot|B_n|. }[/math]
Литература
- N. Balakrishnan (1992). Handbook of the Logistic Distribution. Marcel Dekker, New York. ISBN 0-8247-8587-8.
- Johnson, N. L., Kotz, S., Balakrishnan N. (1995). Continuous Univariate Distributions. Vol. 2 (2nd Ed. ed.). ISBN 0-471-58494-0.
Для улучшения этой статьи желательно: |